Build AI Pac-Man with Convolutional Neural Network
Problem Statement:
The Ms. Pac-Man environment presents a classic reinforcement learning challenge, requiring an agent to master the game of Ms. Pac-Man. The core objective is to achieve the highest possible score by:
-
Collecting all pellets: The primary goal is to consume all small and large pellets scattered across the maze.
-
Evading ghosts: Four ghosts (Blinky, Pinky, Inky, and Clyde) constantly pursue Ms. Pac-Man, and contact with them results in losing a life.
-
Utilizing power pellets: Consuming large "power pellets" temporarily turns the ghosts vulnerable, allowing Ms. Pac-Man to eat them for bonus points.
-
Strategic navigation: The agent must learn optimal paths through the maze to efficiently collect pellets and avoid or strategically consume ghosts.
The problem specifically involves training an agent to select actions from a discrete space of 9 possible movements (including diagonals and no-operation) based on visual observations of the game screen (an RGB image of 210x160x3 pixels). The challenge is to develop an AI that can learn complex strategies for pathfinding, risk assessment, and timing to maximize its score across various game difficulties and modes, adapting to the dynamic environment presented by the moving ghosts and changing pellet configurations.
Project Details:
Description
Your goal is to collect all of the pellets on the screen while avoiding the ghosts.
Actions
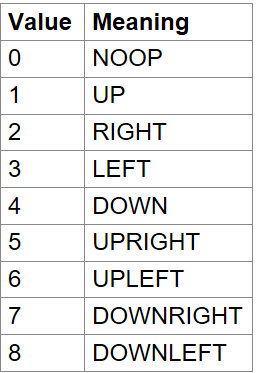
MsPacman has the action space of Discrete(9) with the table below listing the meaning of each action’s meanings. To enable all 18 possible actions that can be performed on an Atari 2600, specify full_action_space=True during initialization or by passing full_action_space=True to gymnasium.make.
Observation Space
Atari environments have three possible observation types:
-
obs_type="rgb" -> observation_space=Box(0, 255, (210, 160, 3), np.uint8)
-
obs_type="ram" -> observation_space=Box(0, 255, (128,), np.uint8)
-
obs_type="grayscale" -> Box(0, 255, (210, 160), np.uint8), a grayscale version of the q”rgb” type
See variants section for the type of observation used by each environment id by default.
Starting State
The lander starts at the top center of the viewport with a random initial force applied to its center of mass.
Episode Termination
The episode finishes if:
-
the lander crashes (the lander body gets in contact with the moon);
-
the lander gets outside of the viewport (x coordinate is greater than 1);
-
the lander is not awake. From the Box2D docs, a body which is not awake is a body which doesn’t move and doesn’t collide with any other body:
-
When Box2D determines that a body (or group of bodies) has come to rest, the body enters a sleep state which has very little CPU overhead. If a body is awake and collides with a sleeping body, then the sleeping body wakes up. Bodies will also wake up if a joint or contact attached to them is destroyed.
-
Project Key Flow Chart for Lunar Landing:
-
Installation of required packages and importing the libraries
-
Installing Gymnasium
-
Importing the Libraries
-
-
Building the AI
-
Creating the Architecture of Neural Network
-
-
Training the AI
-
Setting up the Environment
-
Initializing the Hyperparameters
-
Preprocessing the Frames
-
Implementing the DCQN Class
-
Initializing the DCQN Agent
-
Training the DCQN Agent
-
-
Visualizing the Results
Final Output:
